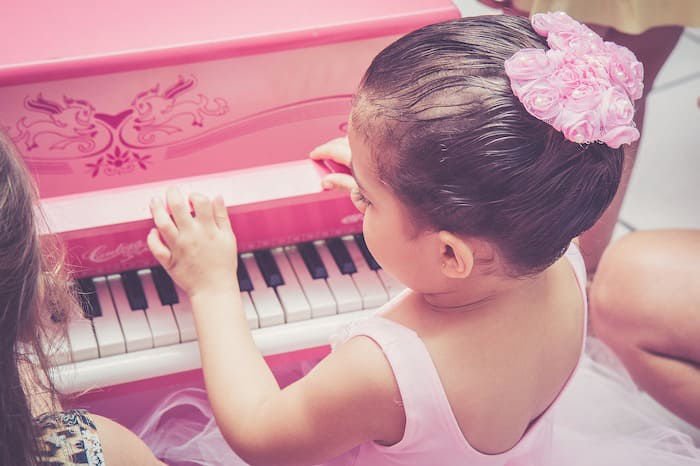
What is music therapy?
What if we used music to accompany children and teenagers with disorders, or mental illnesses? This is the challenge of this new form of support. Not to treat but to accompany the patient in addition to his treatment to, for example, reduce pain, speech disorders, improve social interactions and many other benefits as we will see below.
There are 2 kinds of approaches to music therapy:
– passive; the child listens to music, designed for him/her, by a relative or music therapist who plays an instrument or sings. It is the interaction that counts; a looped CD will not have the same effect.
– active; it is up to the child to come into play, it is he who becomes the master of the musical instrument of his choice: piano, percussion, voice…
Music therapy for all?
“Yes, it is suitable for all people. Adaptation is very simple as long as the person does not have a hearing problem. Moreover, even during a rather active music therapy with singing and playing an instrument, the contraindications are relatively low. In conclusion: music therapy can be applied to most of us. »
Hervé Platel, interview of March 2018 for France Alzeimer.
The benefits of music on our bodies are well proven. But what are the benefits for children with disorders?
We will see here the best known and most relevant to children and adolescents.
Autism Spectrum Disorders X Music
Autism and Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) are part of pervasive developmental disorders (PDDs), which are psychological disorders, due to neurobiological dysfunction and characterized by changes in communication, social interactions, learning and behaviour. The first signs appear during childhood, most often between 18 and 36 months.
700
K persons concerned in France
100
K are less than 20 years old
18
months: the age at which signs begin to appear
Many studies highlighted the effects of music on a sample of children and adolescents with autistic disorders.
Significant improvements were noted in:
– brain stimulation
– concentration and attention
– socialization
– verbal and physical communication
– body coordination
– adaptation
– the parent/child relationship
– stress reduction
That said, it has to be defined on a case-by-case basis, because each child and young adult is different and has a unique response to music.
Let’s take Kodi Lee as an example.
Kodi is blind and has Autistic Spectrum Disorder.
This 22-year-old man caused a sensation a few days ago on the set of America’s Got Talent 2019 by singing and playing the piano.
Her mother tells us: “We discovered that Kodi Lee loved music very early on (…) when you have autism, it’s hard to do what everyone else does, playing music saved your life. »
Watch the video below; you certainly won’t be able to stay out of marble!
Attention Deficit Disorder with Hyperactivity X Music
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder. ADHD is characterized by the presence of inattentive and/or hyperactive-impulsive behaviours and leads to various attention, verbal and motor problems. A loss of self-esteem, dropping out of school and socialization problems are direct consequences of ADHD.
4%
of school children are affected by ADHD
3%
of adults are affected by ADHD
The study of Linda Essiambre of the University of Quebec has been particularly revealing of the music can help to reduce ADHD disorders through benefits, with here, guitar lessons offered to hyperactive children whose behaviours have been evaluated, particularly within their school. A clear improvement was highlighted on:
– the behaviour;
decreased aggressiveness, improved classroom behaviour, observed cohesion between the children studied
– hyperactivity;
improved self-control
– socialization;
sense of responsibility, commitment to collective activities, respect for others, self-esteem
– learning;
motivation for learning French and music, creativity, perseverance, curiosity, attention span…
In particular, the increase in self-esteem should be highlighted. This was very little present at the beginning of the study, although it is directly related to all the other improvements noted.
The Troubles Dys X Music Dys
We usually talk about Dyslexia but Dys disorders include several of them that are often unknown:
– Dyslexia: reading disorders
– Dyspraxia: motor and writing development disorders
– Dyscalculia: number disorders and calculations
– Dysphasia: oral language disorders
6%
at least of the French people concerned by the Dys
4%
at least some students in an age group are dyslexic
3%
are dyspraxic
2%
are dysphasic
Music has proven its worth on Dyslexia in an Inserm study in 2015. Children aged 8 to 11 years, in addition to speech therapy sessions, participated in music sessions twice a week for 2 months. Music can help to reduce disorders through benefits.
At the end of these 2 months, when reading a text, the results were spectacular:
60% of child musicians have improved so much that they have emerged from the criteria of dyslexia!
An easy practice to set up for Dys disorders:
“The sessions do not require any particular expertise from the teachers and there are music therapists or music teachers who are used to these practices. It just needs rhythm! The child should have fun and want to go. And the cost can be quite moderate. But these sessions must be complementary to speech therapy, which has never been abandoned during our study and which remains a cornerstone of management,” says the researcher.
La Touche Musicale allows the simplified learning of the piano in a very intuitive way and can be part of the path of the child and adolescent with disorders with the accompaniment of a music therapist or a trained parent.




 PianoConvert
PianoConvert
 GuitarConvert
GuitarConvert
 SingConvert
SingConvert
 BandConvert
BandConvert
 DrumConvert
DrumConvert
 ViolinConvert
ViolinConvert
 SaxConvert
SaxConvert
 FluteConvert
FluteConvert
 BassConvert
BassConvert
 TrumpetConvert
TrumpetConvert
 OrganConvert
OrganConvert
 PianoGo
PianoGo